The Flooring Expert
High Voltage Suspension Toughed Glass Insulator
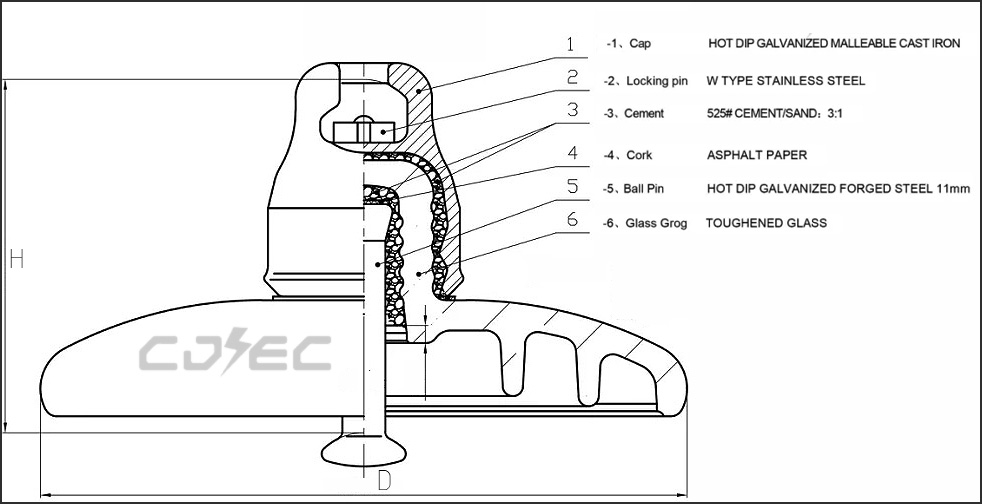
Product Design Drawings
Product Art Photos
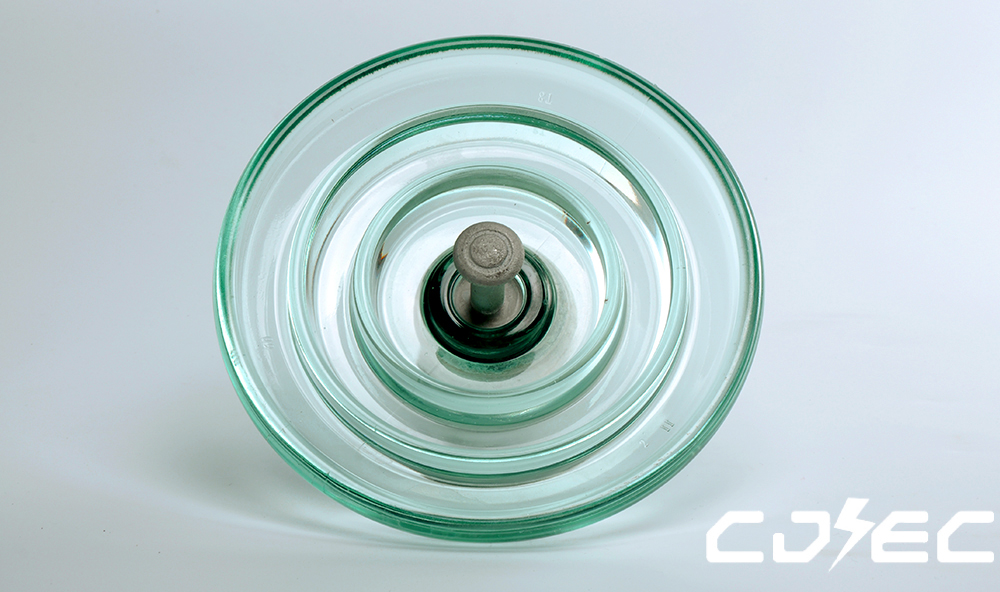
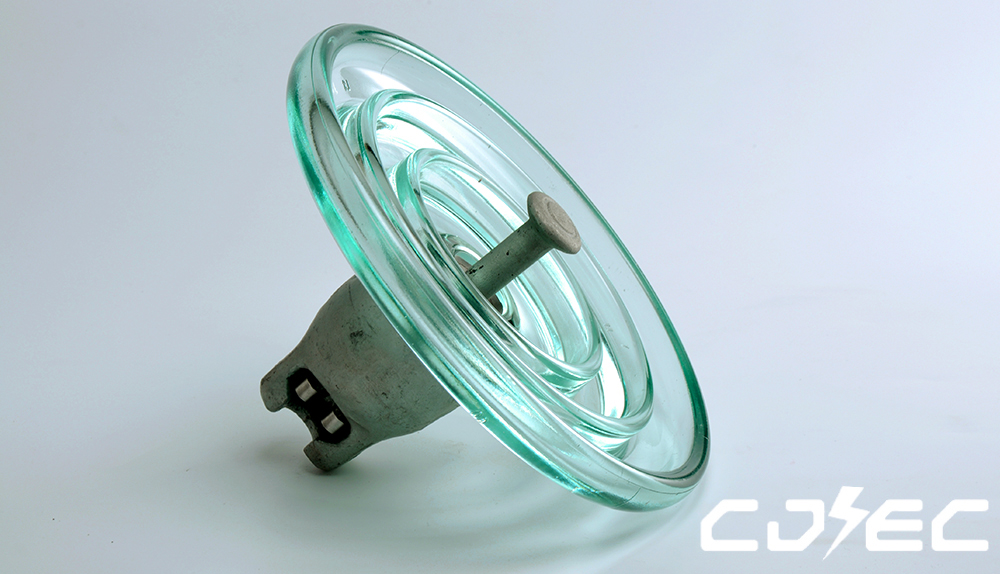
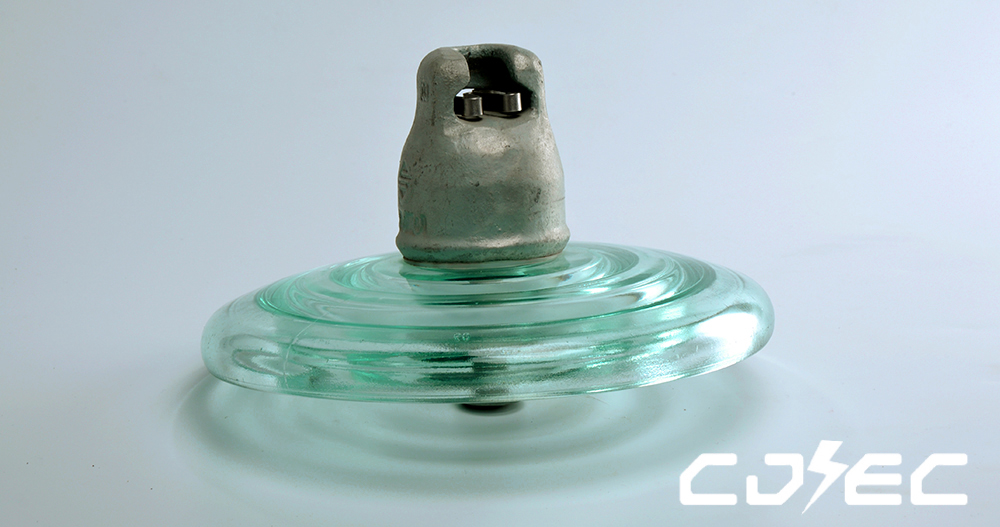
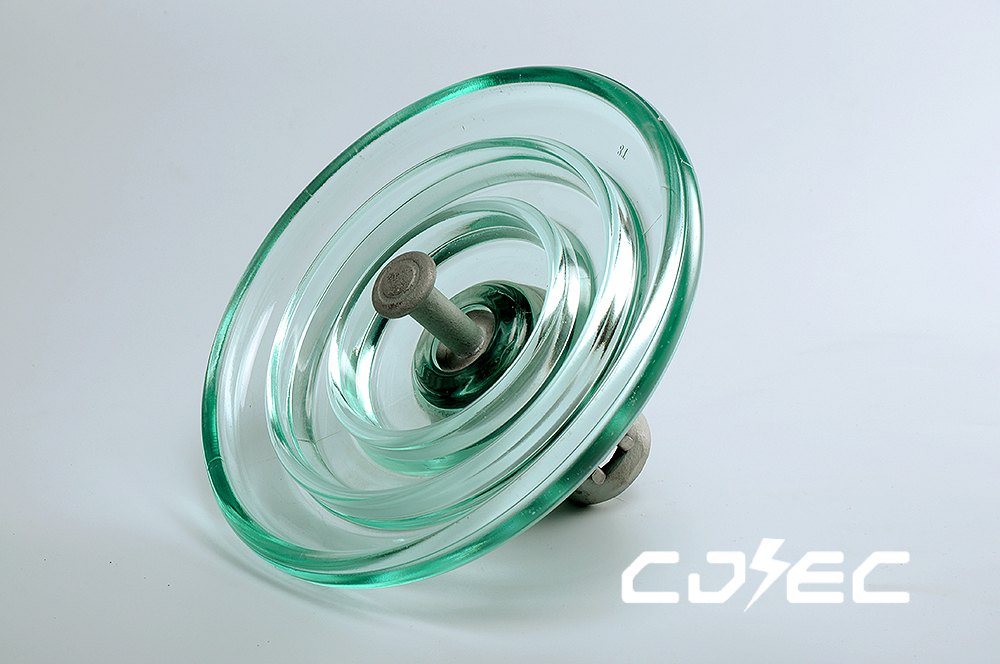




Product Technical Parameters
| IEC designation | U40B/110 | U70B/146 | U70B/127 | U100B/146 | U100B/127 | U120B/127 | U120B/146 | U160B/146 | U160B/155 | U160B/170 | |
| Diameter D | mm | 178 | 255 | 255 | 255 | 255 | 255 | 255 | 280 | 280 | 280 |
| Height H | mm | 110 | 146 | 127 | 146 | 127 | 127 | 146 | 146 | 155 | 170 |
| Creepage distance L | mm | 185 | 320 | 320 | 320 | 320 | 320 | 320 | 400 | 400 | 400 |
| Socket coupling | mm | 11 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Mechanical failing load | kn | 40 | 70 | 70 | 100 | 100 | 120 | 120 | 160 | 160 | 160 |
| Mechanical routine test | kn | 20 | 35 | 35 | 50 | 50 | 60 | 60 | 80 | 80 | 80 |
| Wet power frequency withstand voltage | kv | 25 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 45 | 45 | 45 |
| Dry lightning impulse withstand voltage | kv | 50 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 110 | 110 | 110 |
| Impulse puncture voltage | P.U | 2.8 | 2.8 | 2.8 | 2.8 | 2.8 | 2.8 | 2.8 | 2.8 | 2.8 | 2.8 |
| Power frequency puncture voltage | kv | 90 | 130 | 130 | 130 | 130 | 130 | 130 | 130 | 130 | 130 |
| Radio influence voltage | μv | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Corona visual test | kv | 18/22 | 18/22 | 18/22 | 18/22 | 18/22 | 18/22 | 18/22 | 18/22 | 18/22 | 18/22 |
| Power frequency electric arc voltage | ka | 0.12s/20kA | 0.12s/20kA | 0.12s/20kA | 0.12s/20kA | 0.12s/20kA | 0.12s/20Ka | 0.12s/20Ka | 0.12s/20Ka | 0.12s/20Ka | 0.12s/20Ka |
| Net weight per unit | kg | 2.1 | 3.6 | 3.5 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 6.7 | 6.6 | 6.7 |
Product advantages and disadvantages
1. Glass insulator
Advantages: the mechanical strength of the surface layer of glass insulator is high, the surface is not easy to crack, and the aging speed is slow; It can cancel the live periodic preventive test of insulators during operation, and there is no need to carry out “zero value” detection during operation, so the operation and maintenance cost is low.
Disadvantages: due to the transparency of glass, it is easy to find small cracks and various internal defects and damages during appearance inspection.
2. Ceramic insulator
Advantages: good chemical stability and thermal stability, strong anti-aging ability, good electrical and mechanical properties, and flexible assembly.
Disadvantages: defects are not easy to be found, and they begin to be found only after several years of operation; The zero value detection of ceramic insulators must be carried out one by one on the tower, which requires a lot of manpower and material resources; The probability of accidents caused by lightning stroke and pollution flashover is high.
3. Composite insulator
Advantages: small size, easy maintenance; Light weight and easy installation; High mechanical strength, not easy to break; Excellent seismic performance and good pollution resistance; Fast production cycle and high quality stability.
Disadvantages: anti aging capability is not as good as ceramic and glass insulators, and the production cost is higher than that of ceramic and glass insulators.

Scope of use and specification
1 scope
This standard specifies the general technical requirements, selection principles, inspection rules, acceptance, packaging and transportation, installation and operational maintenance, and operational performance testing for ac overhead line insulators with nominal voltages above 1000V.
This standard is applicable to disk-type suspended porcelain and glass insulators (insulators for short) used in ac overhead power lines, power plants and substations with nominal voltage above 1000Y and frequency 50Hz. The altitude of the installation site must be lower than 1000m, and the ambient temperature must range from -40 ° c to +40 ° c. 2 Normative reference files
The following documents contain provisions which are referred to in this International Standard. All subsequent amendments (excluding errata) or revisions to dated referenced documents do not apply to this standard; however, parties to agreements under this Standard are encouraged to study the availability of the latest version of these documents. For undated references, the latest version applies to this standard. GB311.1-1997.
Insulation coordination for high voltage transmission and transformation equipment (NEQ IEC 60071-1∶1993) GB/T772-2005
Technical specifications for porcelain high-voltage insulators GB/T775.2 — 2003
Insulators – Test methods – Part 2: Electrical test methods GB/T775.3-2006
Insulators – Test methods – Part 3: Mechanical test methods GB/T 1001.1 2003
Overhead line insulators of nominal voltages above 1000V – part 1; Definitions, test methods and criteria for ceramic or glass insulator elements for use in alternating current systems (MOD IEC 60383-1) GB/T 2900.5 2002
Electrical terminology for insulating solids, liquids and gases [EQV IEC60050 (212) : 1990] GB/T 2900.8 1995
Electrical terminology insulators (EQV IEC 60471) GB/T 4056
Structure and dimensions of suspension insulators for high voltage lines (EQV IEC 60120) GB/T 4585-2004
Manual pollution test for high voltage insulators for use in ac systems (IDT IEC 60507; 1991). GB/T7253
Insulators – ceramic or glass insulator elements for use in ac systems for overhead line insulators with nominal voltages above 1000V – characteristics of disk-type suspension insulator elements (mod IEC 60305∶1995)
DLT 557-2005
Impact breakdown testing in air for high voltage line insulators — Definitions, test methods and criteria (MOD IEC 61211:2002) DLT 620
Overvoltage protection and insulation coordination for AC electrical installations DLT 626-2005
Test practice for degraded disc suspension insulators DL/T 812 — 2002
Test method for arc requirements for string insulators for overhead lines with nominal voltages above 1000V (eqv IEC 61467:1997) DL/T 5092-1999
Technical specification for design of 110kV ~ 500%kV overhead transmission lines JB/T3567-1999
Test method for radio interference of high voltage insulators JB/T 4307-2004
Cement cement JB/T 5895 — 1991 for insulator adhesive installation
Guidelines for use of insulators in polluted areas JB/T 8178–1995
Specification for iron caps of suspension insulators – Locking pins for ball-and-socket connections of insulator string elements JB/T 8181-1999
Steel pin JB/T 9677-1999 for disc-type suspension insulators
Exterior quality of glass parts for disc-type suspension glass insulators
JB/T9678-1999
Product Application
Pictures from the Internet
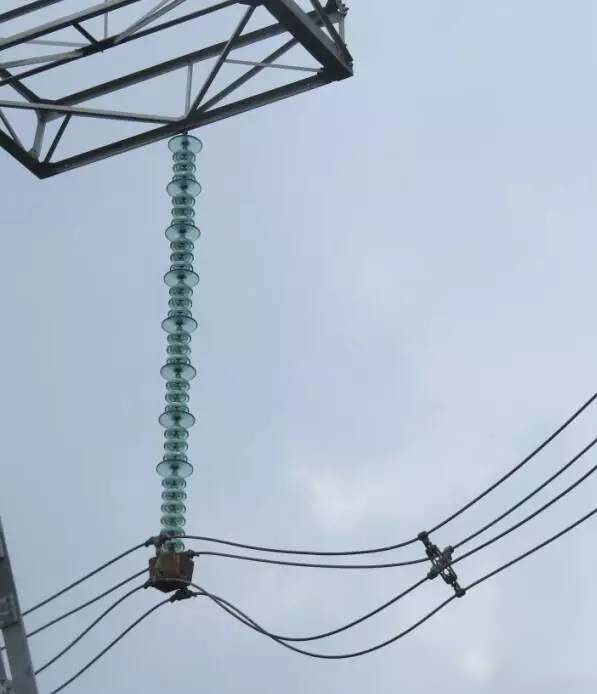
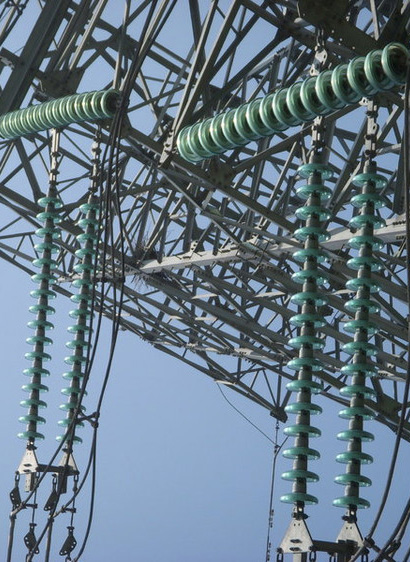



Products categories
WHY CHOOSE US
Since its establishment, our factory has been developing first world class products with adhering the principle
of quality first. Our products have gained excellent reputation in the industry and valuabletrusty among new and old customers..










